Using Agent-Based Modeling to Understand the Emergence and Reproduction of Social Inequalities in Health
Abstract
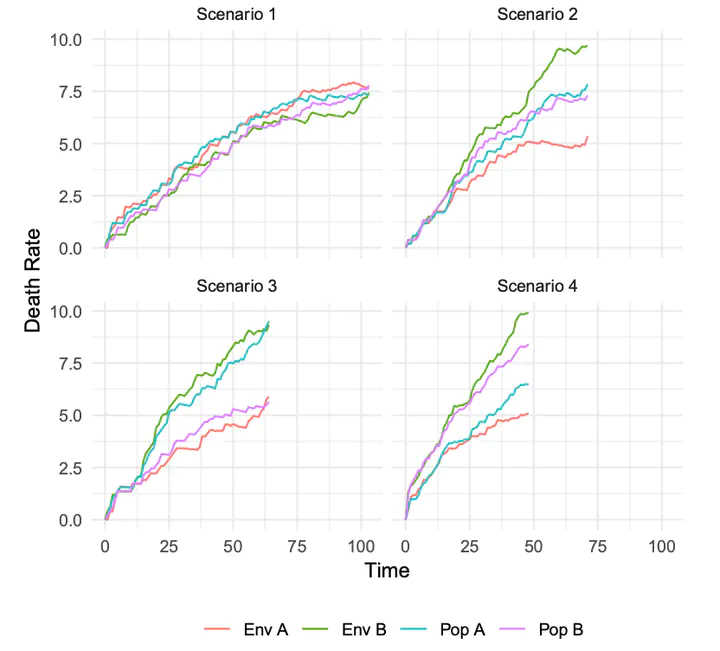
Studies on social inequalities in health present contradictory findings when they attempt to describe and identify the complex societal mechanisms that give rise to poor health outcomes and health inequalities. This work aims to study the mechanism of reproduction of health inequalities among different population groups using agent-based modeling. We combine evidence-based knowledge and survey data to set the simulation model. Our initial findings show that the combination of the most adverse contextual conditions (i.e., negative environmental exposure and the absence of health-care provision) combined with extreme social inequalities in health might increase mortality drastically. The model suggests that, although poor health outcomes may emerge through the action of individual determinants, social inequalities generally emerge and reproduce through non-linear associations and complex multivariate data structures..